The Ultimate Guide to Knee Pain: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment Options
Introduction
Knee pain is a common issue that affects millions of people, from active seniors to busy professionals. Whether it’s a sharp twinge after a long day or a chronic ache that hinders your daily activities, understanding the root causes and finding effective treatments is crucial. In this comprehensive guide, you’ll learn about the various causes of knee pain, recognize common symptoms, and explore a range of treatment options to help you manage and relieve your discomfort.
Causes of Knee Pain
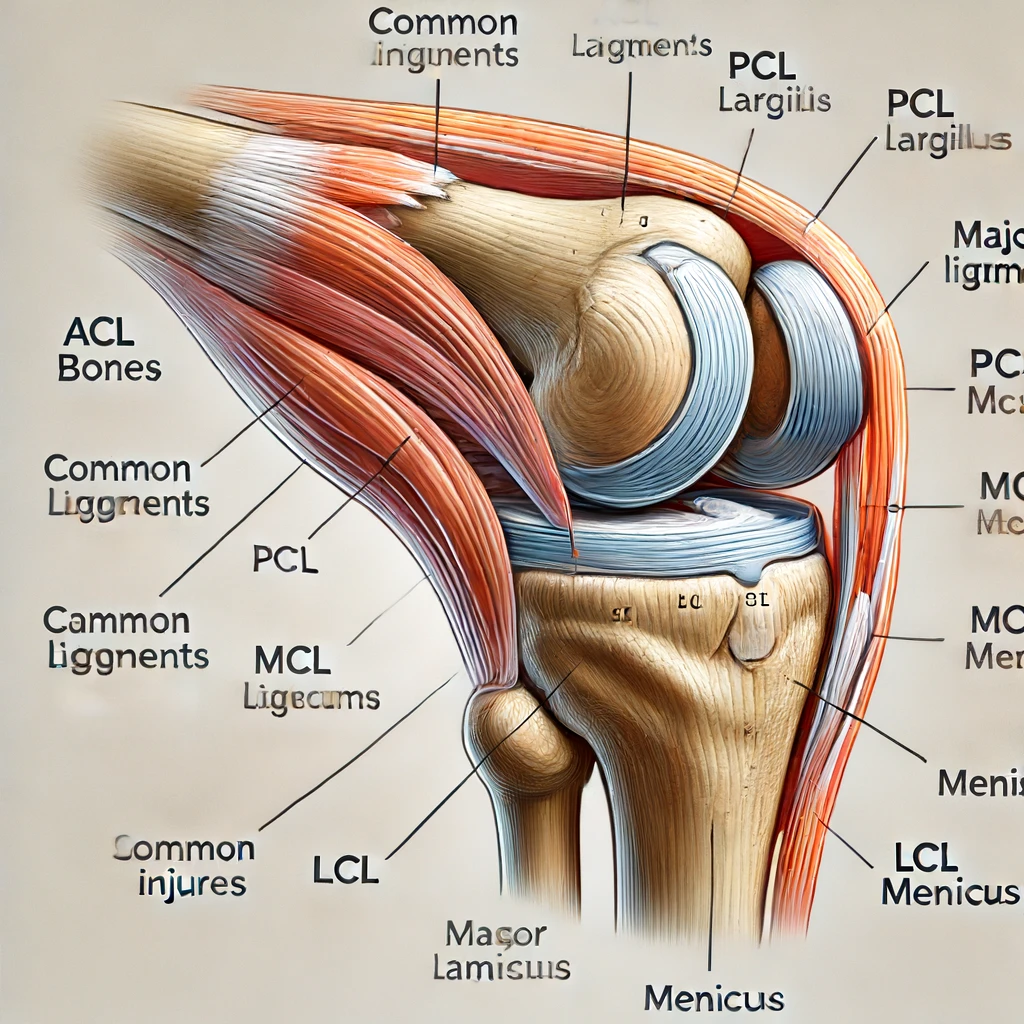
Injuries
Knee pain can result from acute injuries such as ligament tears, meniscus tears, and fractures. For instance, an anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) tear often occurs during sport activities, leading to severe pain and instability. These injuries typically require immediate attention and may involve long-term rehabilitation.
Medical Conditions
Chronic conditions like osteoarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis, and gout are significant contributors to knee pain. According to the CDC, osteoarthritis affects over 32 million adults in the US, causing joint pain and stiffness. Rheumatoid arthritis, an autoimmune disorder, can also cause severe knee pain and inflammation. Gout, a form of arthritis characterized by sudden, severe attacks of pain and swelling, often affects the knees as well.
Lifestyle Factors
Obesity, lack of physical activity, and occupations which require repetitive knee movements, can exacerbate knee pain. Excess weight increases, stress on knee joints, will lead to pain and deterioration over time. Additionally, jobs that involve prolonged standing, heavy lifting, or repetitive bending can strain the knees and contribute to chronic pain.
Symptoms of Knee Pain
Types of Pain
Knee pain can be sharp, dull, or intermittent. Sharp pain often indicates an acute injury, such as a ligament tear or fracture, while dull pain may suggest a chronic condition such as osteoarthritis or bursitis. Intermittent pain might be associated with overuse or specific activities.
Associated Symptoms
Common symptoms accompanying knee pain include swelling, stiffness, redness, and instability. The Mayo Clinic reports that knee instability is a frequent symptom in ligament injuries. Swelling and redness typically indicate inflammation, while stiffness can make it difficult to move the knee through its full range of motion.
Severity and Duration
Understanding the severity and duration of knee pain is essential. Acute pain that is intense and sudden is often due to injury and may require immediate medical attention. Chronic pain lasting more than a few weeks should be evaluated by a healthcare professional to determine the underlying cause and appropriate treatment.
Treatment Options for Knee Pain
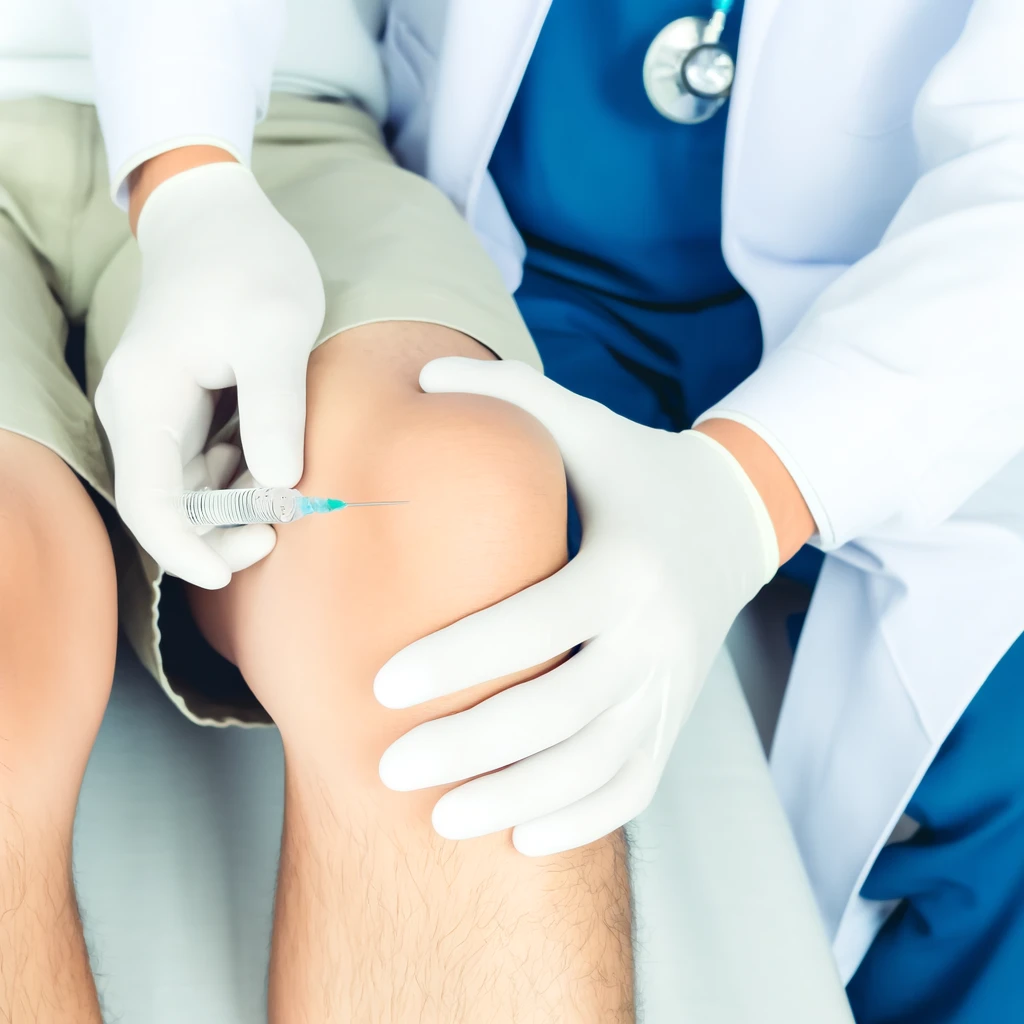
Medical Treatments
Medications, physical therapy, and surgical options are available for more severe cases of knee pain. NSAIDs (nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs) are commonly prescribed to alleviate pain and reduce inflammation. Physical therapy exercises can strengthen the muscles around the knee, improving stability and function. In some cases, surgical interventions such as arthroscopy, partial knee replacement, or total knee replacement may be necessary.
Home Remedies
The RICE method (Rest, Ice, Compression, and Elevation) is a simple yet effective way to manage knee pain at home. Applying ice packs for 20 minutes, several times a day, can significantly reduce inflammation. Resting the knee and avoiding activities that exacerbate pain are crucial. Compression with an elastic bandage can help reduce swelling, and elevating the leg can also minimize fluid buildup.
Alternative Therapies
Alternative treatments like acupuncture, massage, and supplements such as glucosamine and chondroitin can also be beneficial. Studies show that acupuncture can effectively reduce chronic knee pain and improve function. Massage therapy can help relieve muscle tension and improve circulation. Supplements may provide additional support for joint health, although their effectiveness can vary.
Conclusion
Understanding the causes and symptoms of knee pain is crucial for effective management. Whether through home remedies, medical treatments, or alternative therapies, there are various ways to alleviate discomfort and maintain an active lifestyle. If you’re experiencing persistent knee pain, consult with a healthcare professional to explore the best treatment options for your needs. For more information and resources on managing knee pain, visit our website.


